Manufacturing Resilience: Japan's Industrial Sector Defies Odds with 9-Month Growth Streak
Manufacturing
2025-03-24 04:51:08Content
Japan's manufacturing sector continues to face headwinds, as the latest Au Jibun Bank Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) reveals persistent challenges. In March 2025, the index slipped to 48.3, falling short of market expectations and extending a troubling streak of contraction to nine consecutive months.
The preliminary estimates show a modest decline from February's reading of 49.0, underscoring the ongoing struggles within Japan's industrial landscape. Economists had anticipated a slightly better performance, with forecasts pointing to a 49.2 reading, but the actual figures paint a more subdued picture of the country's manufacturing health.
This sustained contraction signals potential economic pressures, suggesting that Japanese manufacturers are grappling with complex challenges such as global supply chain disruptions, shifting market demands, and potentially lingering economic uncertainties.
Investors and policymakers will likely scrutinize these numbers closely, seeking insights into the broader economic implications and potential strategies to reinvigorate the manufacturing sector.
Japan's Manufacturing Sector Struggles: A Deep Dive into Economic Challenges
In the intricate landscape of global economic dynamics, Japan's manufacturing sector continues to navigate turbulent waters, revealing profound challenges that extend far beyond simple economic indicators. The persistent contraction signals deeper structural issues within the world's third-largest economy, prompting critical analysis and strategic reflection.Decoding the Economic Signals: When Manufacturing Speaks Volumes
The Persistent Manufacturing Downturn
Japan's manufacturing ecosystem is experiencing a prolonged period of contraction that demands comprehensive examination. The Au Jibun Bank Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) has now recorded nine consecutive months of decline, painting a nuanced picture of economic resilience and vulnerability. This sustained downturn is not merely a statistical anomaly but a complex narrative of industrial transformation, global supply chain disruptions, and structural economic challenges. The March 2025 reading of 48.3 represents more than just a numerical decline. It encapsulates the intricate challenges facing Japanese manufacturers, including technological adaptation, workforce dynamics, and international competitive pressures. Economists and industry analysts are closely scrutinizing these indicators, recognizing them as critical barometers of broader economic health.Global Context and Comparative Dynamics
The manufacturing contraction cannot be viewed in isolation. It reflects a broader global economic recalibration, where traditional manufacturing powerhouses are confronting unprecedented technological and geopolitical shifts. Japan's experience mirrors similar challenges faced by other advanced economies, highlighting the interconnected nature of modern industrial ecosystems. Technological innovation, automation, and the rapid evolution of global supply chains are fundamentally reshaping manufacturing paradigms. Japanese industries are at a critical juncture, requiring strategic investments in research and development, workforce upskilling, and adaptive manufacturing technologies to remain competitive on the global stage.Economic Implications and Strategic Responses
The persistent manufacturing contraction carries significant implications for Japan's economic strategy. Policymakers and corporate leaders are compelled to develop multifaceted approaches that address structural challenges while fostering innovation and resilience. This involves reimagining industrial policies, investing in emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and robotics, and creating more flexible economic frameworks that can rapidly adapt to changing global conditions. The current economic landscape demands a holistic approach that balances traditional manufacturing strengths with forward-looking strategic initiatives.Technological Transformation and Future Outlook
Japan's manufacturing sector stands at a critical evolutionary point. The current challenges present an opportunity for fundamental reimagination of industrial capabilities. Emerging technologies such as advanced robotics, precision manufacturing, and sustainable production methods offer promising pathways for revitalization. The integration of digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and advanced manufacturing techniques represents a potential renaissance for Japanese industry. By embracing these transformative approaches, manufacturers can potentially reverse the current contraction and establish new competitive advantages in the global marketplace.Workforce and Innovation Ecosystem
Central to Japan's manufacturing renaissance is the development of a robust innovation ecosystem. This requires significant investments in human capital, educational infrastructure, and collaborative research environments. The future of manufacturing will be defined by the ability to attract, develop, and retain top technological talent. Universities, research institutions, and industry must forge stronger partnerships to create a dynamic knowledge exchange that drives continuous innovation. The workforce of the future must be agile, technologically proficient, and capable of navigating increasingly complex global manufacturing landscapes.RELATED NEWS
Manufacturing

Manufacturing Renaissance: Can America Reclaim Its Industrial Crown?
2025-04-11 12:30:24
Manufacturing
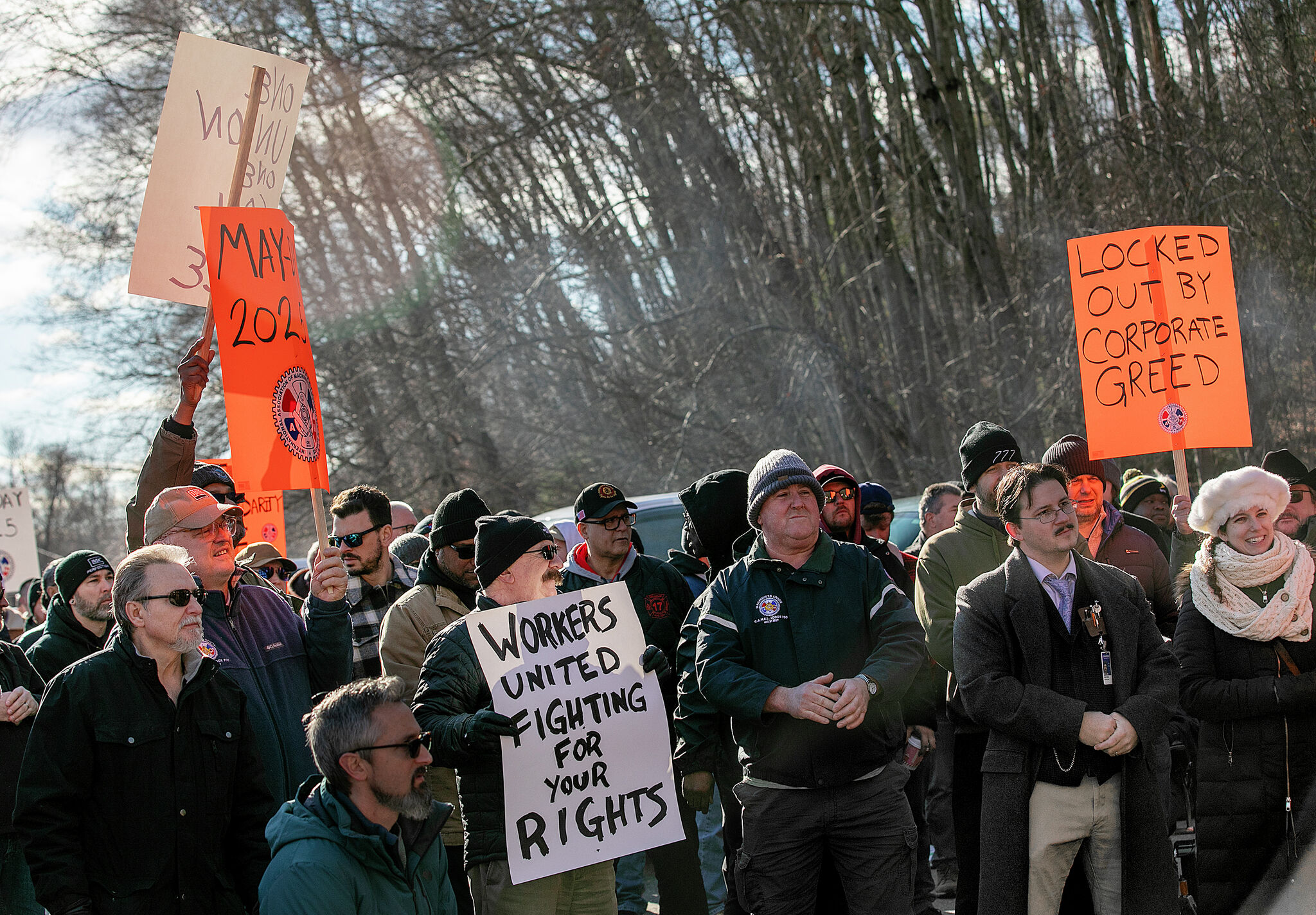
Precision vs. Paycheck: Pratt & Whitney Workers Demand Fair Compensation in High-Stakes Contract Showdown
2025-03-29 09:00:00
Manufacturing

Beyond Borders: How New Vision Display Transforms Malaysian Manufacturing Landscape
2025-05-02 05:01:00




