Shocking Revelation: Your Daily Routine Could Be a Silent Health Killer
Lifestyle
2025-04-29 02:38:29Content
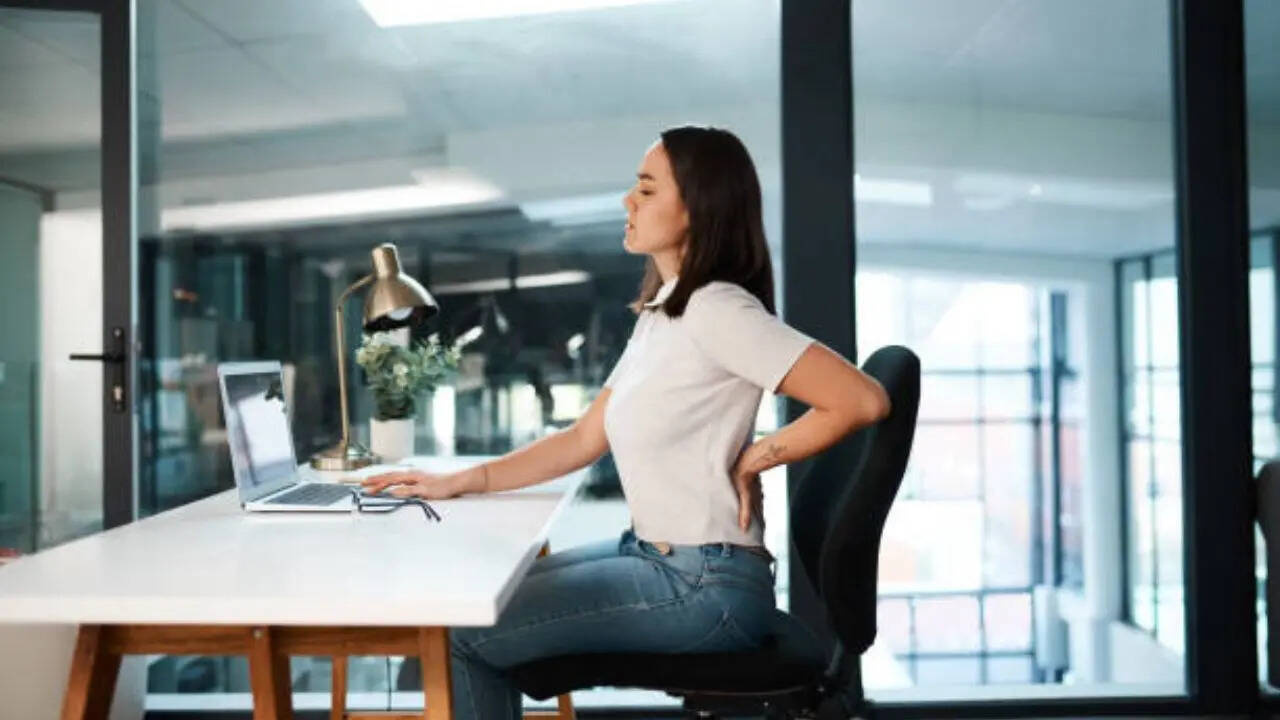

In the modern workplace, your seemingly harmless desk job might be silently undermining your health. Prolonged sitting has emerged as a critical health risk, comparable to the dangers once associated with smoking. Medical experts now warn that extended periods of sedentary behavior can trigger a cascade of serious health complications.
Dr. Stephen Williams, a renowned cardiologist at NYU Langone, understands the profound impact of a stationary lifestyle. Despite working in a traditionally sedentary profession, he actively combats the risks by incorporating movement throughout his day.
The potential health consequences of excessive sitting are alarming. From cardiovascular diseases and obesity to mental health challenges like anxiety and depression, the risks extend far beyond mere physical discomfort. Joint deterioration and muscular weakness are additional concerns that can significantly impact long-term well-being.
Recognizing the importance of staying active, professionals like Dr. Williams recommend simple strategies to break the cycle of prolonged sitting. These include taking short walking breaks, using standing desks, stretching regularly, and consciously incorporating movement into daily routines.
As workplace health becomes increasingly prioritized, understanding and mitigating the risks of a sedentary lifestyle is crucial for maintaining optimal physical and mental health.
The Silent Killer: How Your Desk Job is Destroying Your Health
In the modern workplace, a sedentary lifestyle has become an insidious threat lurking beneath the surface of seemingly harmless professional routines. As technology advances and office jobs dominate the employment landscape, millions of workers unknowingly compromise their physical and mental well-being through prolonged periods of inactivity.Unmasking the Deadly Consequences of Sitting: Your Body's Hidden Battle
The Physiological Breakdown of Prolonged Sedentary Behavior
The human body is an intricate machine designed for movement, yet contemporary work environments systematically undermine our biological imperatives. When individuals remain stationary for extended periods, complex metabolic processes begin to deteriorate. Muscle groups become dormant, cardiovascular efficiency diminishes, and metabolic rates plummet dramatically. Research indicates that individuals who sit for more than eight hours daily experience significant cellular-level changes that accelerate aging and increase systemic inflammation. Physiological studies reveal that prolonged sitting triggers a cascade of negative health consequences. Blood circulation becomes compromised, leading to reduced oxygen transportation and potential blood clot formation. Muscular atrophy occurs progressively, weakening core stabilizer muscles and creating imbalances that can result in chronic pain syndromes and reduced mobility.Psychological Implications of Sedentary Work Environments
Beyond physical deterioration, extended periods of immobility profoundly impact mental health. Neurochemical research demonstrates that sedentary behaviors correlate directly with increased risks of anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline. The brain's neuroplasticity becomes compromised when physical movement is restricted, potentially leading to reduced creativity, diminished problem-solving capabilities, and increased stress responses. Psychological studies suggest that individuals trapped in sedentary work environments experience higher levels of cortisol, the primary stress hormone. This hormonal imbalance can trigger a domino effect of mental health challenges, including reduced emotional resilience and increased susceptibility to burnout.Cardiovascular Risks and Metabolic Syndrome
Cardiologists and metabolic specialists have identified sitting as a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Prolonged immobility disrupts insulin sensitivity, increases triglyceride levels, and reduces high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. These metabolic disturbances create a perfect storm for developing chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Advanced medical imaging techniques have demonstrated that individuals maintaining sedentary lifestyles experience accelerated arterial calcification and reduced endothelial function. These microscopic changes represent early warning signs of potential cardiovascular complications that may emerge decades later.Strategic Interventions and Lifestyle Modifications
Combating the detrimental effects of prolonged sitting requires a multifaceted approach. Healthcare professionals recommend implementing dynamic workplace strategies that prioritize movement and physical engagement. Ergonomic interventions such as standing desks, active sitting chairs, and scheduled movement breaks can mitigate potential health risks. Comprehensive wellness programs should integrate regular physical activity, mindfulness practices, and biomechanical assessments to create holistic health strategies. Employers and individuals must recognize that movement is not a luxury but a fundamental requirement for maintaining optimal physiological and psychological functioning.Technological Solutions and Emerging Research
Cutting-edge research explores innovative technological interventions designed to counteract sedentary lifestyle challenges. Wearable devices, artificial intelligence-driven movement tracking, and personalized health algorithms represent promising frontiers in addressing prolonged sitting's negative consequences. Emerging studies suggest that targeted micro-movements, even as brief as two-minute intervals every hour, can significantly interrupt metabolic decline and restore cellular functionality. These discoveries challenge traditional understanding and provide hope for individuals trapped in sedentary work environments.RELATED NEWS
Lifestyle

From Drab to Dramatic: Kitchen Transformation Stuns with Moody Makeover
2025-04-19 16:45:00
Lifestyle
Kirstie Allsopp's Controversial Confession: Influencer Calls Out TV Star's Provocative Online Outburst
2025-03-30 12:33:48






