Inside Apple's Manufacturing Maze: Why Making iPhones in the U.S. Remains an Impossible Dream
Manufacturing
2025-04-28 13:15:44Content

The Complex Challenge of Localizing iPhone Manufacturing: Why U.S. Production Remains Elusive
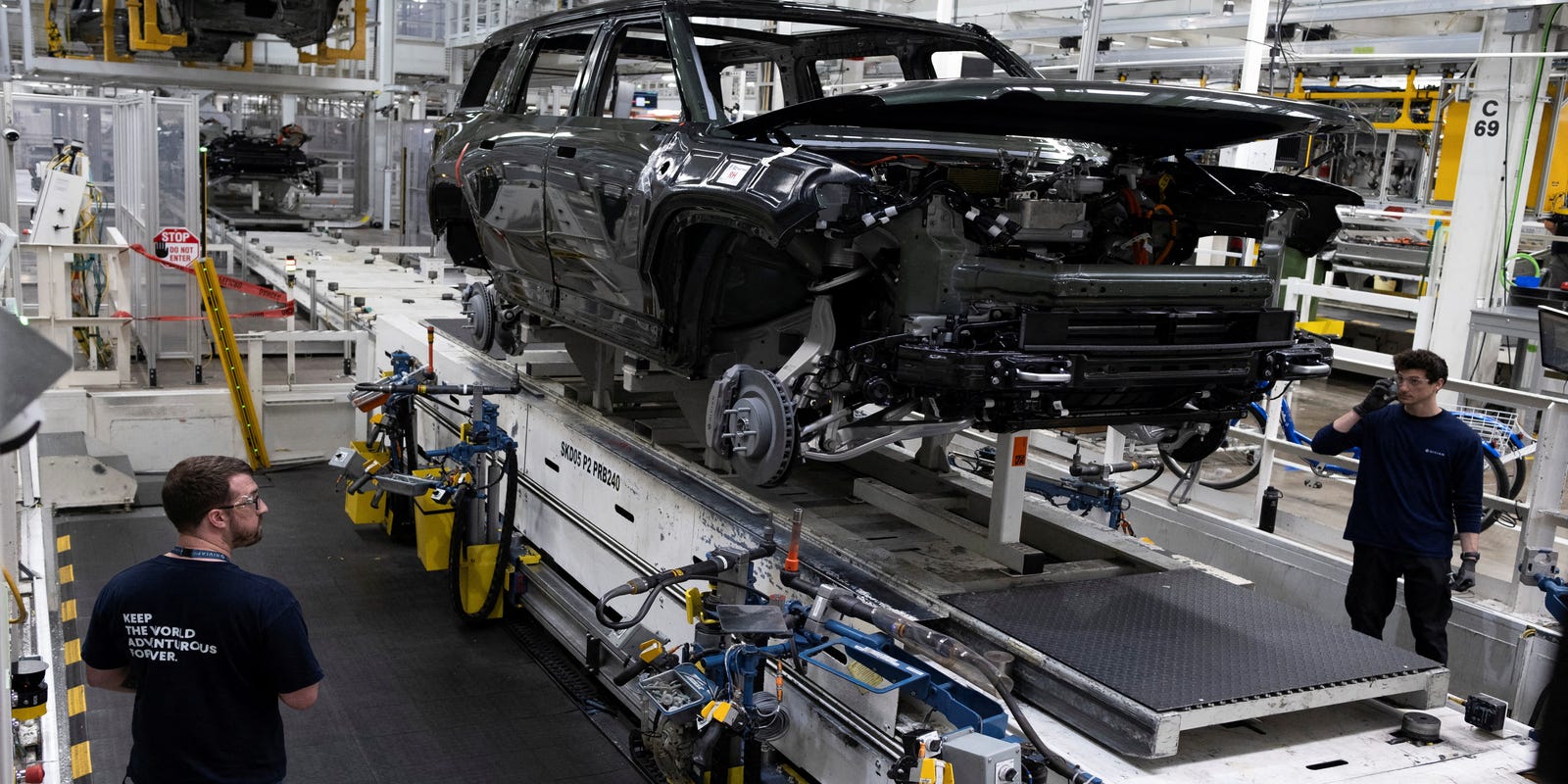
A comprehensive investigation has uncovered the intricate obstacles preventing Apple from fully transitioning iPhone production to the United States. The sheer complexity of manufacturing, involving an astounding 2,700 individual components, makes a complete domestic production shift an extraordinary challenge.
The intricate global supply chain that currently supports iPhone manufacturing has been meticulously developed over decades, creating a sophisticated ecosystem that cannot be easily replicated within U.S. borders. Each of the thousands of precision parts requires specialized manufacturing techniques, advanced infrastructure, and a highly skilled workforce that currently exists primarily in international manufacturing hubs.
While the concept of reshoring manufacturing sounds appealing, the practical realities reveal a far more nuanced landscape. The technological precision, cost-effectiveness, and established manufacturing networks make the current international production model extremely difficult to replace with a domestic alternative.
Ultimately, the dream of complete U.S.-based iPhone production remains more of a theoretical aspiration than a near-term feasible reality, highlighting the complex global nature of modern electronics manufacturing.
The Impossible Dream: Why iPhone Manufacturing Can't Escape Global Supply Chains
In the complex world of global technology manufacturing, Apple's iPhone production represents a intricate dance of international collaboration, engineering prowess, and economic strategy that defies simple relocation or nationalist manufacturing ambitions.Unraveling the Manufacturing Complexity Behind Every iPhone
The Global Manufacturing Ecosystem
The iPhone's production is a testament to the interconnected nature of modern technological manufacturing. With over 2,700 individual components sourced from multiple continents, the device represents a sophisticated global supply network that cannot be easily replicated within a single national boundary. Each component requires specialized manufacturing capabilities, precision engineering, and intricate supply chain logistics that have been meticulously developed over decades. Manufacturers around the world have invested billions in creating specialized infrastructure that supports the production of smartphone components. Countries like China, Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan have developed unique technological ecosystems that enable the hyper-precise manufacturing required for cutting-edge electronic devices. These ecosystems cannot be rapidly reconstructed or transplanted without massive financial investment and years of technological development.Economic and Technological Barriers to Domestic Production
Attempting to relocate iPhone production to the United States would require an unprecedented economic transformation. The current manufacturing infrastructure in Asia has developed through decades of strategic investment, government support, and a highly skilled workforce trained specifically in advanced electronics manufacturing. American manufacturing would need to overcome significant challenges, including higher labor costs, limited existing infrastructure, and a workforce that lacks the specialized skills required for such intricate electronics production. The cost of rebuilding an entire manufacturing ecosystem would be astronomical, potentially rendering iPhone production economically unfeasible. Existing Asian manufacturers have achieved economies of scale that would be extremely difficult to replicate in the United States, making domestic production not just challenging, but potentially prohibitively expensive.Technological Precision and Supply Chain Complexity
Each iPhone represents a marvel of engineering that requires microscopic precision across thousands of components. The current global supply chain has been optimized through years of refinement, with manufacturers specializing in specific technological niches that contribute to the final product. Semiconductor fabrication, battery production, display manufacturing, and intricate electronic component creation require highly specialized facilities that cannot be quickly or easily duplicated. The technological know-how embedded in the current manufacturing process represents intellectual capital that has been developed through decades of research, development, and incremental improvements. Attempting to rapidly transfer or recreate this knowledge base would require not just financial investment, but also a fundamental reimagining of technological education and industrial strategy.Geopolitical and Strategic Considerations
Beyond pure manufacturing challenges, the iPhone's production is deeply intertwined with complex geopolitical relationships. The current manufacturing network represents a delicate balance of international cooperation, trade agreements, and strategic economic partnerships. Attempting to dramatically restructure this network would not just be a technological challenge, but a significant diplomatic and economic undertaking with far-reaching consequences. The global nature of iPhone production reflects a broader trend in modern technology manufacturing, where innovation and production are inherently international processes that transcend traditional national boundaries. Any attempt to dramatically localize such a complex product would require a fundamental reimagining of global technological collaboration.RELATED NEWS
Manufacturing
Manufacturing Renaissance: Walz Celebrates Philips' Minnesota Comeback
2025-04-10 17:08:02
Manufacturing

Breaking: The GLP-1 Revolution - Why Biopharma Needs a Radical Manufacturing Makeover
2025-02-25 13:05:00
Manufacturing

Unlocking Productivity: How Eye Tracking Technology is Revolutionizing Workplace Efficiency
2025-04-23 08:00:04