Prehistoric Comeback: The Risky Science of Resurrecting Earth's Lost Giants
Science
2025-04-25 13:01:35Content

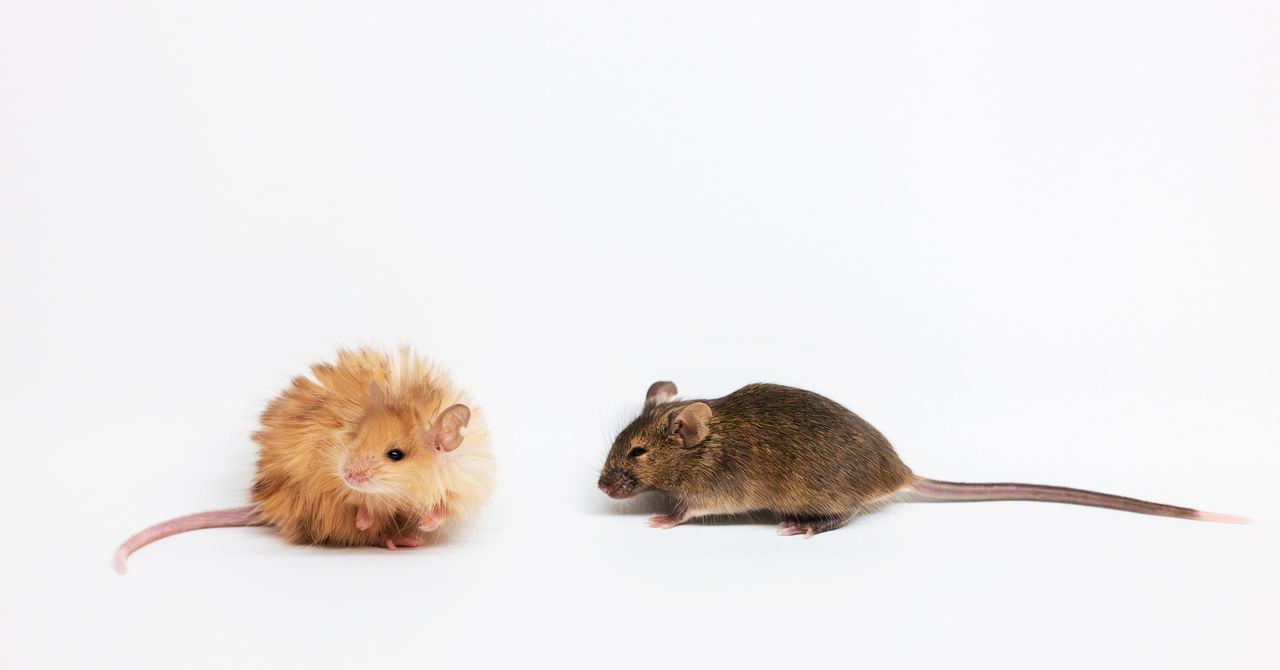
In a groundbreaking scientific breakthrough, researchers have successfully created three "dire wolf" pups, sparking both excitement and controversy in the scientific community. This remarkable achievement has ignited hope that de-extinction—bringing back long-lost species—might be more than just a distant dream.
The creation of these prehistoric canine embryos represents a potential turning point in genetic research, offering a tantalizing glimpse into the possibility of resurrecting extinct animals. However, the scientific world is far from unanimous in its enthusiasm. Prominent researchers have expressed serious reservations about the ethical and ecological implications of such a scientific endeavor.
While the prospect of seeing creatures that disappeared thousands of years ago roam the earth again is undeniably thrilling, experts warn of complex challenges. Reintroducing extinct species could have unpredictable consequences for existing ecosystems, potentially disrupting delicate environmental balances that have evolved over centuries.
Despite the concerns, the dire wolf project represents a fascinating intersection of cutting-edge genetic technology and paleontological research. As scientists continue to push the boundaries of what's scientifically possible, the debate surrounding de-extinction remains as complex and nuanced as the genetic processes themselves.
Resurrecting Prehistoric Predators: The Groundbreaking Science of De-Extinction
In the cutting-edge realm of genetic engineering, scientists are pushing the boundaries of biological possibility, exploring revolutionary techniques that could potentially bring extinct species back to life. The recent breakthrough involving dire wolf genetic reconstruction represents a monumental leap forward in our understanding of prehistoric life restoration and genetic manipulation.Unleashing the Power of Genetic Resurrection: A Scientific Frontier Beyond Imagination
The Genetic Engineering Revolution
Modern biotechnology has reached an unprecedented milestone in genetic reconstruction, challenging traditional limitations of scientific research. Researchers are now employing sophisticated molecular techniques to decode and potentially resurrect species that vanished centuries ago. The dire wolf project represents more than a scientific experiment; it's a profound exploration of genetic potential that could fundamentally transform our understanding of biological preservation and species restoration. The intricate process involves meticulously extracting ancient DNA fragments, reconstructing genetic sequences, and utilizing advanced reproductive technologies. Scientists must navigate complex ethical and biological challenges, balancing technological innovation with responsible scientific practice.Technological Challenges in De-Extinction
Reconstructing extinct species demands extraordinary technological sophistication. Genetic researchers must overcome multiple complex obstacles, including degraded DNA preservation, incomplete genetic sequences, and the intricate process of cellular reprogramming. The dire wolf reconstruction represents a delicate balance between cutting-edge genetic engineering and paleogenetic research. Molecular biologists employ advanced computational modeling and genetic sequencing techniques to piece together fragmented genetic information. This process requires unprecedented precision, combining computational algorithms with biological expertise to recreate genetic blueprints of long-extinct species.Ethical Implications and Scientific Controversy
The potential resurrection of prehistoric species generates significant scientific and ethical debate. While some researchers view de-extinction as a groundbreaking opportunity to restore lost biodiversity, others raise critical concerns about potential ecological disruptions and unintended consequences. Prominent scientists argue that reintroducing extinct species could have profound and unpredictable impacts on existing ecosystems. The delicate balance of contemporary environmental systems might be fundamentally altered by the sudden reappearance of prehistoric predators like dire wolves.Biological and Ecological Considerations
Reconstructing prehistoric species involves more than genetic manipulation. Researchers must consider complex ecological interactions, potential environmental adaptations, and the long-term sustainability of reintroduced species. The dire wolf project serves as a critical case study in understanding the intricate relationships between genetic reconstruction and ecological integration. Sophisticated research methodologies combine genetic engineering, paleontological insights, and ecological modeling to assess the potential impacts of species resurrection. Each reconstructed organism represents a unique scientific experiment with far-reaching implications for our understanding of biological diversity.Future Prospects and Scientific Horizons
The dire wolf reconstruction project symbolizes humanity's expanding scientific capabilities. As genetic technologies continue to advance, researchers are increasingly optimistic about the potential to resurrect and potentially preserve endangered or extinct species. This groundbreaking research opens unprecedented scientific frontiers, challenging our traditional understanding of biological limitations and offering glimpses into potential future scientific achievements. The ability to reconstruct prehistoric life represents a transformative moment in scientific exploration, bridging past and present through the remarkable power of genetic engineering.RELATED NEWS
Science

Science Spectacular: Maine's Premier Festival Transforms Bangor This Week
2025-03-19 22:09:40
Science

Breaking: Your Inner Emotional Blueprint Decoded - The Science That Could Transform Anxious Minds
2025-03-29 16:14:29